
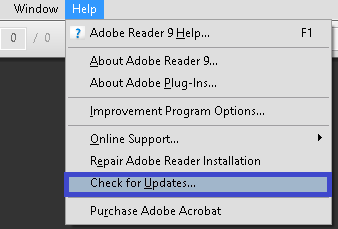
- #WORD FOR MAC THIS DOCUMENT COULD NOT BE SAVED PDF CODE#
- #WORD FOR MAC THIS DOCUMENT COULD NOT BE SAVED PDF PLUS#
The purpose of using plain text today is primarily independence from programs that require their very own special encoding or formatting or file format. For example, all the problems of Endianness can be avoided (with encodings such as UCS-2 rather than UTF-8, endianness matters, but uniformly for every character, rather than for potentially-unknown subsets of it). The use of plain text rather than binary files enables files to survive much better "in the wild", in part by making them largely immune to computer architecture incompatibilities. For example, an SVG file can express drawings or even bitmapped graphics, but is still plain text. The particular content is irrelevant to whether a file is plain text.
#WORD FOR MAC THIS DOCUMENT COULD NOT BE SAVED PDF CODE#
Thus, representations such as SGML, RTF, HTML, XML, wiki markup, and TeX, as well as nearly all programming language source code files, are considered plain text. SGML, RTF, HTML, XML, and TEX are examples of rich text fully represented as plain text streams, interspersing plain text data with sequences of characters that represent the additional data structures."Īccording to other definitions, however, files that contain markup or other meta-data are generally considered plain text, so long as the markup is also in directly human-readable form (as in HTML, XML, and so on).
#WORD FOR MAC THIS DOCUMENT COULD NOT BE SAVED PDF PLUS#
In contrast, styled text, also known as rich text, is any text representation containing plain text plus added information such as a language identifier, font size, color, hypertext links, and so on.Plain text is a pure sequence of character codes plain Un-encoded text is therefore a sequence of Unicode character codes.Put another way, translating a plain text file to a character encoding that uses entirely different numbers to represent characters does not change the meaning (so long as you know what encoding is in use), but for binary files such a conversion does change the meaning of at least some parts of the file. For example, a file or string consisting of "hello" (in whatever encoding), following by 4 bytes that express a binary integer that is not just a character(s), is a binary file, not plain text by even the loosest common usages. Plain text is also sometimes used only to exclude "binary" files: those in which at least some parts of the file cannot be correctly interpreted via the character encoding in effect. As Unicode-based encodings such as UTF-8 and UTF-16 become more common, that usage may be shrinking. In principle, plain text can be in any encoding, but occasionally the term is taken to imply ASCII. For example, that could exclude any indication of fonts or layout (such as markup, markdown, or even tabs) characters such as curly quotes, non-breaking spaces, soft hyphens, em dashes, and/or ligatures or other things. The term is sometimes used quite loosely, to mean files that contain only "readable" content (or just files with nothing that the speaker doesn't prefer). Plain text is different from formatted text, where style information is included from structured text, where structural parts of the document such as paragraphs, sections, and the like are identified and from binary files in which some portions must be interpreted as binary objects (encoded integers, real numbers, images, etc.). It may also include a limited number of "whitespace" characters that affect simple arrangement of text, such as spaces, line breaks, or tabulation characters (although tab characters can "mean" many different things, so are hardly "plain"). file contents) that represent only characters of readable material but not its graphical representation nor other objects ( floating-point numbers, images, etc.). In computing, plain text is a loose term for data (e.g. Text file with portion of The Human Side of Animals by Royal Dixon, displayed by the command cat in an xterm window


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
